SSH 端口转发
SSH 除了登录服务器,还有一大用途,就是充当两台服务器之间的跳板,然后得益于ssh的加密通信,额外也能使得原本不加密的通信变成加密通信。这个功能称为端口转发(port forwarding)和 SSH 隧道(tunnel)技术。
端口转发有两个主要作用:
- 作为数据通信的跳板,绕过网络防火墙,比如端口和IP限制。
- 将不加密的数据放在 SSH 安全连接里面传输,增加了安全性,比如走ssh隧道访问 http 接口,数据传输就都会被加密。
端口转发有三种:
- 本地转发, 常用于访问企业防火墙后面服务器的的资源/服务,绕过防火墙的拦截。
- 远程转发,应用开发人员常用于短时开放app给其他人访问,让他人能访问开发人员本地电脑上开发部署的的测试服务,如一个接近完成的web应用演示。
- 动态转发,常用于解除对中间人或者目标服务对本机的IP限制,利用远程机器的IP访问目标服务,再通过ssh回传。
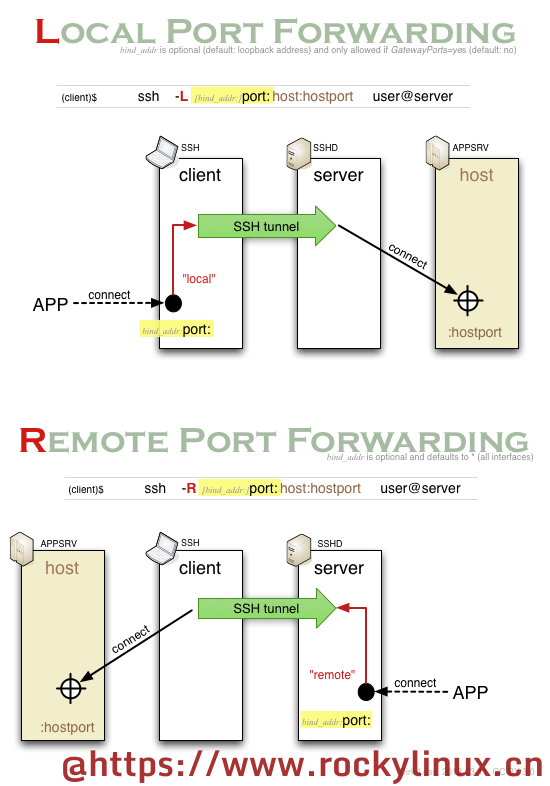
本地转发 -L
本地转发(local forwarding)指的是,在 本机 监听一个新的端口,将发往该端口的所有通信数据都通过 SSH 服务器,转发到指定的远程服务器的端口。这种情况下,SSH 服务器只是一个作为跳板的中介,用于连接本地计算机无法直接连接的远程服务器。本地转发是在本地计算机建立的转发规则。
例如:我们有三台机器 server1:192.168.222.11 server2:192.168.222.112 server3:192.168.222.113, server2 server3 都在防火墙后面,但规则允许外界通过ssh协议访问 server2, server2 和 server3 可以正常通信, server1 不能直接访问server3。
正在加载 Flowchart 图表...
一个列子: 在本机监听一个新的端口3307,将这个端口收到的数据流量通过与SSH主机august@192.168.222.112建立的SSH隧道, 转发到 远程的 192.168.222.113:3306 主机和端口上。然后就能通过访问 localhost:3307 实现 访问 在防火墙后面无法直接访问的 mysql数据库了(192.168.222.113:3306)。
ssh -N -f -L 3307:192.168.222.11:3306 august@192.168.222.112
# -N -f 后面介绍-L [bind_address:]port:host:hostport
-L [bind_address:]port:remote_socket
-L local_socket:host:hostport
-L local_socket:remote_socket
Specifies that connections to the given TCP port or Unix socket on the local (client) host are to be forwarded to the given host and port,
or Unix socket, on the remote side. This works by allocating a socket to listen to either a TCP port on the local side, optionally bound
to the specified bind_address, or to a Unix socket. Whenever a connection is made to the local port or socket, the connection is forwarded
over the secure channel, and a connection is made to either host port hostport, or the Unix socket remote_socket, from the remote machine.
Port forwardings can also be specified in the configuration file. Only the superuser can forward privileged ports. IPv6 addresses can be
specified by enclosing the address in square brackets.
By default, the local port is bound in accordance with the GatewayPorts setting. However, an explicit bind_address may be used to bind the
connection to a specific address. The bind_address of “localhost” indicates that the listening port be bound for local use only, while an
empty address or ‘*’ indicates that the port should be available from all interfaces.解释:
ssh -L [bind_address:]port:server3:server3port username@server2
ssh -L [bind_address:]本地监听端口:目标主机:目标端口 username@jumhost
# 实现功能:主机1 访问localhost:port <====> server2 <---> server3:server3port
# server3 也可以是 server2 自己一张经典的示意图,可以轻松的帮你理解什么是 port forward.
解除限制
OpenSSH 默认只让使用 localhost / 本地环回接口访问转发的端口,即只能在ssh命令运行的机器server1上访问这个转发端口。有两种方式解除这种限制:
- SSH 命令选项
-g可以用来解除这种限制,使用后就会允许任何机器访问这个转发端口了(也需要这些机器能访问到server1,没有被防火墙拦截)。 - SSH 客户端配置文件(ssh_config))的GatewayPorts 能控制这一功能,将其值改成 yes 也可以达到相同效果。
#server1 上运行
ssh -N -f -g -L 3307:192.168.222.113:3306 username@192.168.222.112
# server1 访问 localhost:3307 没有问题
# 这次使用server2进行访问测试
curl -v telnet://192.168.222.11:3307使用场景
远程服务器部署了一个服务,假如是Nginx,该服务器再防火墙后面,且没有公网IP,暂时还没有做应用发布。部署测试期间 给该服务指定了域名和端口, test-service.example.com,端口443, TLS 证书也已经申请并配置完成。
或者是单机部署的 gitlab(10.10.0.1) 做迁移测试,已经将备份数据恢复到了新机器10.10.0.2,gitlab-new.example.com 上,一切已准备就绪,怎么进行gitlab功能测试呢?
这种时候我们都需要访问这个新部署的服务(nginx or gitlab),Nginx在很多时候都可以用curl直接在部署的机器上测试,但是大型服务的验证不方便简单的用curl进行测试,那我们该如何实现在本地浏览器上访问远程主机上部署的服务呢?
This is SSH local port forward comes into play!
在本地终端运行如下命令开启一个ssh隧道,将访问本机443端口的流量,通过与jumphost的ssh链接,发送到 gitlab-new服务器的gitlab服务。
ssh -NfL 443:gitlab-new-host-ip:gitlab-port username@jumphost再在 hosts 文件中添加映射
127.0.0.1 gitlab-new.example.com然后在浏览器上 你就可以访问 https://gitlab-new.example.com,查看各种状态了。 你的 其他服务比如registry 使用的域名也一并映射一下。
测试没有问题,你就可以放心的进行下一步,应用发布了!
多个服务端口转发
ssh -L 443:gitlab-new-host-ip:gitlab-port -L 80:nginxserver:nginxport -N -f username@jumphost非标ssh端口和密钥
ssh -L 443:gitlab-new-host-ip:gitlab-port -N -f -p2222 -i /path/to/key username@jumphost远程转发 -R
远程转发指的是在远程 SSH 服务器上建立的转发规则。与本地端口转发的数据流动方向相反,应用是通过访问远程服务的端口来访问ssh命令发起本地的机器。建立本地计算机到远程 SSH 服务器的隧道以后,本地转发是通过本地计算机访问远程 SSH 服务器,而远程转发则是通过远程 SSH 服务器访问本地计算机。它的命令格式如下
例如:我们有三台机器 server1:192.168.222.11 server2:192.168.222.112 server3:公网IP, server1 server2 都在本地,防火墙规则允许server1用ssh协议访问公网 server3, server1 和 server2 都没有公网IP, server3 不能直接访问server1 和server3 因为他们没有公网IP,内网不通。
正在加载 Flowchart 图表...
命令如下:
# server1 上运行
ssh -N -R [bind_address:]remote-port:target-host:target-port username@server3
ssh -N -R remote-port:target-host:target-port remotehost
# bind_address可以不设置,remote-port是远程server3上新设置的监听端口号
# target-host:target-port 可以是server1 本身,也可以是server1可以访问的其他机器 比如server2 及其端口
# 实现目标是 访问server2的port端口,数据会通过ssh隧道转发到target-host的target-port端口上注意:OpenSSH服务器对于远程端口转发的设定,默认只接受远程主机server3本机上的应用发起的请求。想要从其他连接到server3的设备发起请求,需将「sshd_config」文件中「
GatewayPorts」选项后的「no」修改为「yes」。注意这里是 sshd_config 不是 ssh_config。
实际用例
开发人员使用本地电脑开发了小程序,还没有开发完成,甚至没有部署到测试环境,此时需要向需求方演示当前已有功能。本地电脑是没有公网IP的,共用的IP也随时变化,但是开发人员拥有或者需求方提供了带有公网IP的服务器。
此时就可以使用远程转发实现让需求方查看小程序的功能。
# 开发人员本地电脑运行一下命令
ssh -NfR 80:localhost:80 username@RemotePublicIP
## 然后 需求方就可以从任意位置访问开发人员本地电脑80端口的服务
curl http://RemotePublicIP常用选项
-N -f -T -t的使用
-N Do not execute a remote command. This is useful for just forwarding ports. Refer to the description
of SessionType in ssh_config(5) for details.
-f Requests ssh to go to background just before command execution. This is useful if ssh is going to ask
for passwords or passphrases, but the user wants it in the background. This implies -n. The recom‐
mended way to start X11 programs at a remote site is with something like ssh -f host xterm.
If the ExitOnForwardFailure configuration option is set to “yes”, then a client started with -f will
wait for all remote port forwards to be successfully established before placing itself in the back‐
ground. Refer to the description of ForkAfterAuthentication in ssh_config(5) for details.
-T Disable pseudo-terminal allocation.
-t Force pseudo-terminal allocation. This can be used to execute arbitrary screen-based programs on a
remote machine, which can be very useful, e.g. when implementing menu services. Multiple -t options
force tty allocation, even if ssh has no local tty.-N不执行命令,只做端口转发。如果不使用该选项,会打开一个ssh会话窗口-f放入后台运行-T不分配 PTY,此时SSH 使用 pipes 而不是终端进行通信,好处是避免了终端的转义比如 控制字符~和line ending. 这在传输 二进制文件时很有用。但是如果你使用vim top等需要pty配合的软件时,就不适合使用-T,这种时候应该使用-t。-t强制分配PTY,有些sudo配置 (e.g., requiretty in /etc/sudoers) 也需要PTY
-o
如果你开始使用 ssh转发,你会发现一个问题,就是时间稍长一点,或者网络情况有点波动,隧道就不能持续工作了!
-o option
Can be used to give options in the format used in the configuration file. This is useful for specifying options for which there is no separate command-line flag. For full details of the
options listed below, and their possible values, see ssh_config(5).
ServerAliveInterval
ServerAliveCountMax
TCPKeepAlive
ServerAliveCountMax
Sets the number of server alive messages (see below) which may be sent without ssh(1) receiving any messages back from the server. If this
threshold is reached while server alive messages are being sent, ssh will disconnect from the server, terminating the session. It is im‐
portant to note that the use of server alive messages is very different from TCPKeepAlive (below). The server alive messages are sent
through the encrypted channel and therefore will not be spoofable. The TCP keepalive option enabled by TCPKeepAlive is spoofable. The
server alive mechanism is valuable when the client or server depend on knowing when a connection has become unresponsive.
The default value is 3. If, for example, ServerAliveInterval (see below) is set to 15 and ServerAliveCountMax is left at the default, if
the server becomes unresponsive, ssh will disconnect after approximately 45 seconds.
ServerAliveInterval
Sets a timeout interval in seconds after which if no data has been received from the server, ssh(1) will send a message through the en‐
crypted channel to request a response from the server. The default is 0, indicating that these messages will not be sent to the server, or
300 if the BatchMode option is set (Debian-specific). ProtocolKeepAlives and SetupTimeOut are Debian-specific compatibility aliases for
this option.
TCPKeepAlive
Specifies whether the system should send TCP keepalive messages to the other side. If they are sent, death of the connection or crash of
one of the machines will be properly noticed. This option only uses TCP keepalives (as opposed to using ssh level keepalives), so takes a
long time to notice when the connection dies. As such, you probably want the ServerAliveInterval option as well. However, this means that
connections will die if the route is down temporarily, and some people find it annoying.
The default is yes (to send TCP keepalive messages), and the client will notice if the network goes down or the remote host dies. This is
important in scripts, and many users want it too.
To disable TCP keepalive messages, the value should be set to no. See also ServerAliveInterval for protocol-level keepalives.ServerAliveInterval保活数据包发送等待时间,在服务器在这个时间内没有发来数据后,通过ssh隧道发送一个消息给服务器请求服务器回复,默认值是0代表不发送保活数据ServerAliveCountMax没有收到服务器回复时 最大发送消息次数,配置interval使用ServerAliveInterval * ServerAliveCountMax时间内没有收到服务器的任何信息后从ssh客户端侧断开ssh链接TCPKeepAlive反应比较慢
动态转发 -D
动态转发指的是,本机监听一个端口,在本机与 SSH 服务器之间创建了一个隧道连接,然后访问本机监听端口的通信都通过这个加密隧道连接进行转发。本地端口和ssh隧道建立关系,所有访问这个端口的流量都走ssh隧道从远程机器出去。
例如:我们有三台机器 server1:192.168.222.11 server2:192.168.222.112 server3:192.168.222.113, server2 server3 都在防火墙后面,但规则允许外界通过ssh协议访问 server2, server2 和 server3 可以正常通信, 出于某些原因 server1 不能直接访问server3。
正在加载 Flowchart 图表...
ssh -CND [bind_address:]local-port remote-host上面的命令中,-D表示动态转发,local-port是本地端口,remote-host 是 SSH 服务器,-C表示ssh隧道对数据进行压缩传输。
# 命令行使用
curl --proxy socks5://localhost:8080 https://server3:443
curl -x socks5://localhost:8080 https://server3:443你也可以在浏览器或者操作系统中配置 socks5代理。
使用场景
应用层代理: 如访问某个网段未发布的一组服务,这组服务暂时不方便从外部访问,但是可以从某个特定机器访问。访问当前网络可能被阻止的网站或服务(例如,突破地域限制)。
安全浏览:在公共网络上保护您的在线活动隐私,通过远程 SSH 服务器路由所有流量,加密所有 Web 流量,隐藏真实 IP 地址,提高匿名性。
这几个场景本质都是代理!











