概述
本章,您将学习 MySQL 中有关 DQL 的知识。
在 MySQL 基础篇的整个知识架构中,DQL 的内容最多也最常使用,学习时应该重点掌握与训练。
DQL 主要包含以下内容:
- 条件查询
- 排序查询
- 函数
- 连接查询
- 嵌套查询
- 分页查询
- 联合查询
受限于篇幅,本篇文档只说明连接查询。
连接查询 - 又称多表查询,指的是当查询的字段来自于多个表时,需要进行表的连接。
连接的分类
根据表之间连接的不同,可以划分为:
-
内连接
- 等值连接
- 非等值连接
- 自连接
-
外连接
- 左外连接
- 右外连接
- 全外连接
- 交叉连接
内连接
内连接的结果集不区分表的书写先后顺序,其本质其实就是数学中的 交集 概念。
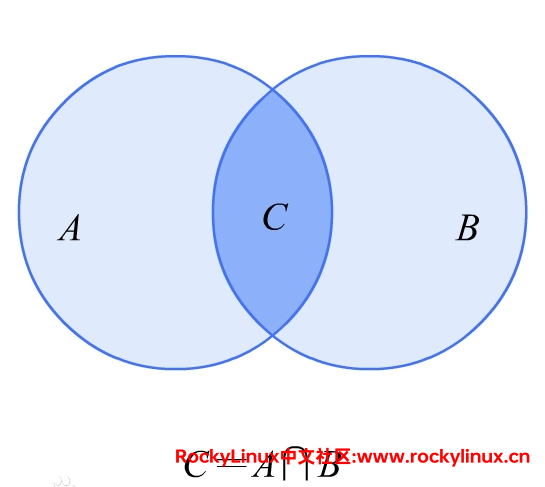
SQL 92标准的内连接
假设现在库中有两张表:
dep 表中的字段与数据如下:
| dep_no | name |
|---|---|
| 1 | 财务 |
| 2 | 管理 |
| 3 | 行政 |
| 4 | 办公 |
dep_emp 表中的字段与数据如下:
| dep_no | emp_no | salary |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1001 | 100 |
| 1 | 1002 | 200 |
等值连接
等值连接 - 即依据 where 后面的等值筛选条件来连接多张表,连接之后组成一张临时的新表。例如:
select * from dep,dep_emp where dep.dep_no=dep_emp.dep_no;执行过程如下:
- 拿第一张表的第一行数据去匹配另外一张表的所有数据
- 拿第一张表的第二行数据去匹配另外一张表的所有数据
- 以此类推
结果如下:
| dep_no | name | dep_no(1) | emp_no | salary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 财务 | 1 | 1001 | 100 |
| 1 | 财务 | 1 | 1002 | 200 |
由于两张表有同名的字段,因此可在查询列表中添加表名来区分,例如:
select dep.dep_no from dep,dep_emp where dep.dep_no=dep_emp.dep_no; 回到具体的 world 库,假设需要查询城市名称和国家名称之间的对应关系。这里很明显需要用到 city 表和 country 表:
use world;
# 明显,我们需要使用 city 表的 CountryCode 字段与 country 表的 code 字段作为等值筛选条件
select city.name as 城市名,country.name 城市所在的国家 from city,country where city.countrycode=country.code;输出如下:
城市名 城市所在的国家
Oranjestad Aruba
Kabul Afghanistan
Qandahar Afghanistan
Herat Afghanistan
Mazar-e-Sharif Afghanistan
Luanda Angola
Huambo Angola
Lobito Angola
Benguela Angola
Namibe Angola
South Hill Anguilla
The Valley Anguilla
Tirana Albania
Andorra la Vella Andorra
....前面提到,多张表等值连接之后会组成一张临时的新表,换言之,and、like、group by、having、order by、is null等关键字也能用于这张新表。
非等值连接
这里的非等值即:
- 大于
- 大于等于
- 小于
- 小于等于
- 不等于
其执行过程:
- 拿第一张表的第一行数据去匹配另外一张表的所有数据
- 拿第一张表的第二行数据去匹配另外一张表的所有数据
- 以此类推
例如:
select city.name,country.name from city,country where city.CountryCode<>country.code and city.name="kabul"; 自连接
自连接 - 即表进行自我连接
emp 表的字段与数据:
| employee_id | name | manager_id |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | chen | (null) |
| 101 | franklee | 100 |
假设我需要知道员工编号为 101 的员工名称与其领导人名称,就需要进行自连接:
select
a.employee_id,
a.name,
b.name
from
emp as a,
emp as b
where
a.manager_id = b.employee_id
and a.employee_id = 101;SQL 99标准的内连接
SQL 99标准的内连接语法如下:
select 查询列表 from 表1 [连接类型] join 表2 on 连接条件;其中内连接的关键字为 inner。
等值连接
查询城市名称与国家名称之间的对应关系,两者的语法对比如下:
# SQL 92
select city.name,country.name from city,country where city.CountryCode=country.code;
# SQL 99
select city.name,country.name from city inner join country on city.CountryCode=country.code;非等值连接
# SQL 92
select
a.name,
b.name
from
city a,
country b
where
a.CountryCode <> b.code
and a.name = "kabul";
# SQL 99
select
a.name,
b.name
from
city a
inner join country b on a.CountryCode <> b.code
where
a.name = "kabul";自连接
# SQL 92
select
a.employee_id,
a.name,
b.name
from
emp as a,
emp as b
where
a.manager_id = b.employee_id
and a.employee_id = 101;
# SQL 99
select
a.employee_id,
a.name,
b.name
from
emp as a
inner join emp as b on a.manager_id = b.employee_id
where
a.employee_id = 101;外连接
到了外连接这里,表的书写先后顺序非常重要(根据先后顺序区分为主表与从表)。执行过程:
- 拿主表的第一行数据去匹配另外一张表的所有数据
- 拿主表的第二行数据去匹配另外一张表的所有数据
- 以此类推
左外连接
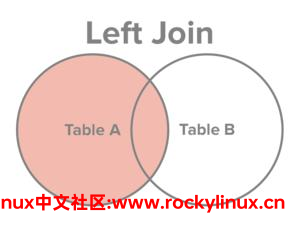
还是拿这两张表来说明。
dep 表中的字段与数据如下:
| dep_no | name |
|---|---|
| 1 | 财务 |
| 2 | 管理 |
| 3 | 行政 |
| 4 | 办公 |
dep_emp 表中的字段与数据如下:
| dep_no | emp_no | salary |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1001 | 100 |
| 1 | 1002 | 200 |
# 以 dep 为主表
select
a.name,
b.emp_no,
b.salary
from
dep a
left join dep_emp b on a.dep_no = b.dep_no;结果为:
财务 1001 100
财务 1002 200
管理
行政
办公在上面的示例中移除共有的交集部分:
select
a.name,
b.emp_no,
b.salary
from
dep a
left join dep_emp b on a.dep_no = b.dep_no
where
b.dep_no is null;右外连接
和左外连接一样,只不过主表与从表发生了变化。
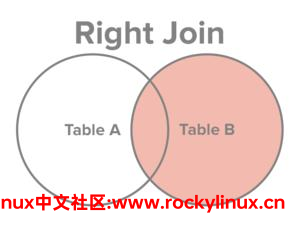
例如:
select
a.name,
b.emp_no,
b.salary
from
dep a
right join dep_emp b on a.dep_no = b.dep_no;全外连接
其实就是数学当中的 并集 概念。
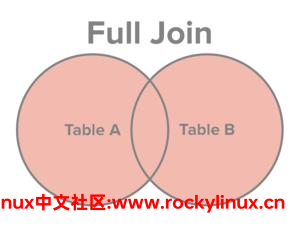
需要注意的是,MySQL 不支持全外连接。在有些 RDBMS 中,关键字为 full join 和 on
假设现在有支持全外连接的 RDBMS,现在有 a 表和 b 表。
a 表的字段与数据:
| id | name |
|---|---|
| 1 | zhang |
| 2 | li |
| 3 | wang |
b 表的字段与数据:
| id | job | parent_id |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 23 | 1 |
| 2 | 34 | 2 |
| 3 | 34 | 4 |
select a.*,b.* from a full join b on a.id=b.parent_id;输出为 4 条记录:
ID NAME ID JOB PARENT_ID
1 zhang 1 23 1
2 li 2 34 2
3 wang null null null
null null 3 34 4交叉连接
交叉连接,又称笛卡尔乘积,使用 cross join 关键字且没有 on 关键字。
笛卡尔乘积(Cartesian product)是指两个集合 X 和 Y 的乘积。
例如,有 A 和 B 两个集合,它们的值如下:
- A = {1,2}
- B = {3,4,5}
集合 A×B 和 B×A 的结果集分别表示为:
A×B={(1,3), (1,4), (1,5), (2,3), (2,4), (2,5) };
B×A={(3,1), (3,2), (4,1), (4,2), (5,1), (5,2) };
实际情况下,使用非常少:
select a.*,b.* from a cross join b;










